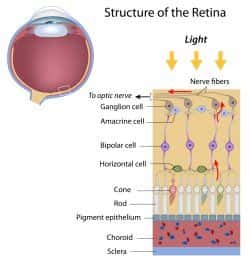
Retinal disorders are conditions that affect the layer of tissue at the back of the eye, known as the retina. This important part of the eye responds to light and passes on images to the brain. All retinal disorders affect your vision in some way, but some can also lead to blindness.
Macular degeneration. Also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), this condition affects the center part of the retina, the macula. This area is needed for the sharp, central vision that is used during everyday activities such as driving, reading or working with tools. This condition is a leading cause of vision loss in people over the age of 60 years old. Treatment can slow the loss of vision, but it will not restore vision that has already been lost.
Diabetic eye disease. The high blood sugar (glucose) levels that occur with diabetes can also affect vision. One type of diabetic eye disease is diabetic retinopathy, which affects the blood vessels in the retina. This can lead to blurry or double vision, blank spots in the vision and pain in one or both eyes. Diabetics may also be at higher risk of developing other eye conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Retinal detachment. This medical emergency happens when the retina pulls or lifts off of its normal position. It can cause symptoms such as floaters in the field of vision, light flashes and the feeling of a “curtain” in the way of your vision. If not treated right away, a retinal detachment can lead to permanent blindness in that eye.
Retinoblastoma. This cancer of the retina is generally uncommon; although, it is the most common type of eye cancer in children. The cancer starts in the cells of the retina, but can spread to other parts of the body (metastasize).
Macular pucker. Scar tissue on the macula can make the central vision become blurry and distorted. Although the symptoms are similar, macular pucker is not the same as age-related macular degeneration. The symptoms of a macular pucker are usually mild and do not require treatment. Sometimes, the scar tissue can fall off the retina on its own, and the vision will return to normal.
Macular hole. This condition is caused by a small break in the macula, which leads to blurriness and distortion in the central vision. Related to aging, this condition usually happens in people over the age of 60. Some macular holes close up on their own while others require surgery to help improve vision.
Floaters. These are specks, or “cobwebs,” that appear in the field of vision. Unlike scratches on the cornea, which follow your eye movements, floaters can drift even when the eyes are not moving. Most people have some floaters and have no problem with their vision. A sudden increase in the number of floaters, though, can indicate a more serious eye problem such as retinal detachment.
If you notice a change in your vision or simply have not undergone a routine eye ex
Visit our Office
4649 Planz Rd.
Bakersfield, CA 93309
